low flow low gradient aortic stenosis guidelines
Ad Review gradient measurement data from studies of the Evolut PRO system. Aortic stenosis AS is defined as a peak aortic jet velocity.

Paradoxical Low Flow Low Gradient Severe Aortic Stenosis A Distinct Disease Entity Heart
Low flow low gradient aortic stenosis with preserved LVEF.
. Mean gradient 40 mmHg peak aortic velocity 4 ms and aortic valve area AVA 1 cm 2 or an indexed AVA 06 cm 2 m 2. Aortic stenosis AS is defined as severe in the presence of. However up to 40 of patients have a discrepancy between gradient and AVA ie.
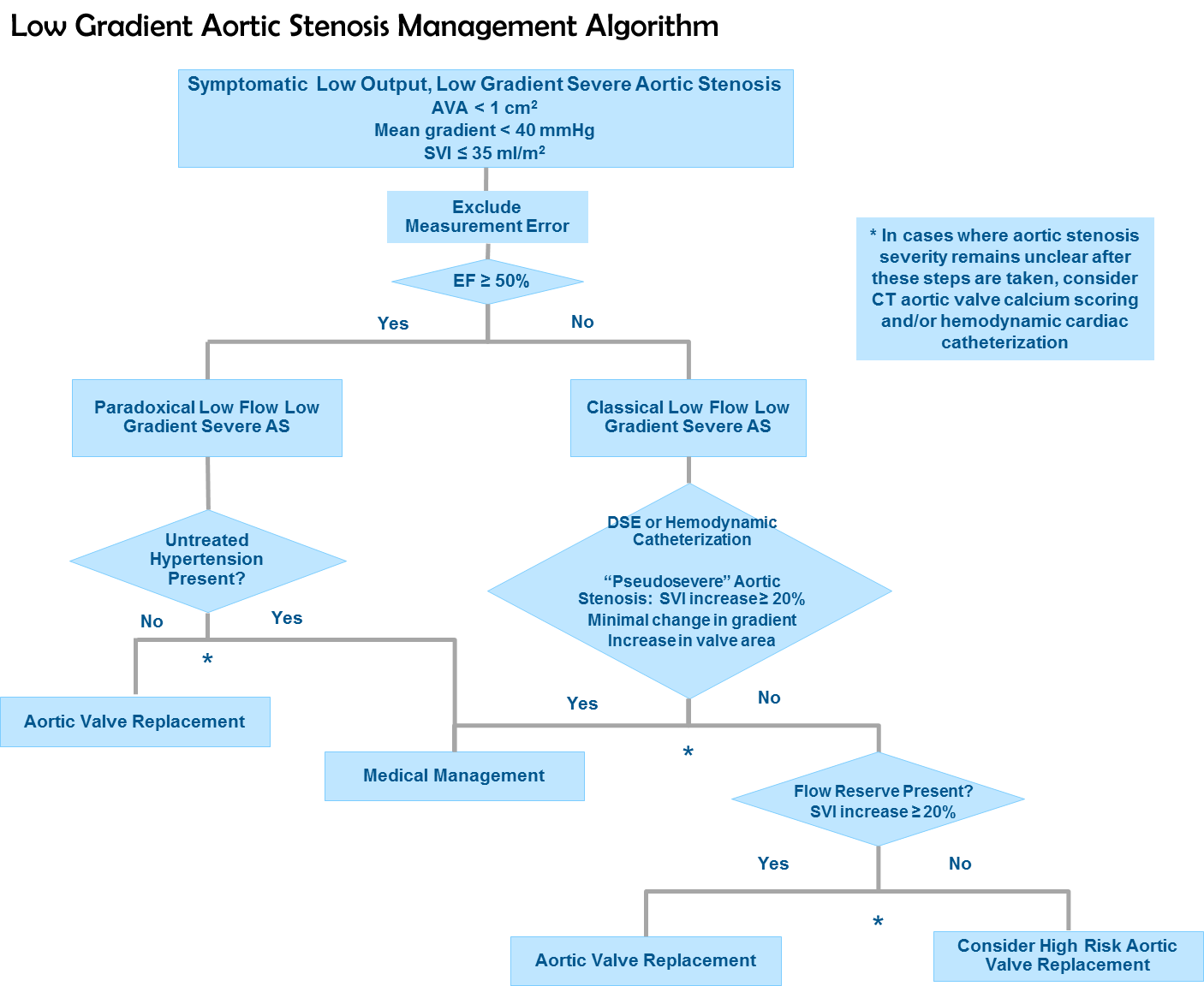
AS grading algorithm- an integrated and stepwise approach. Low-flow low-gradient LF-LG aortic stenosis AS may occur with depressed or preserved left ventricular ejection fraction LVEF and both situations are among the most challenging encountered in patients with valvular heart disease. Low gradient low flow aortic stenosis.
A squared function of flow and may thus be pseudo-normalized and underestimate stenosis severity in presence of low flow. On the other hand the AVA may be. On the other hand the AVA may be.
Association of Cardiothoracic Surgery guidelines12severe. Low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis is a difficult entity to diagnose and treat. Ad Pioneers in Minimally Invasive Procedures for the Treatment of Mitral Valve Disease.
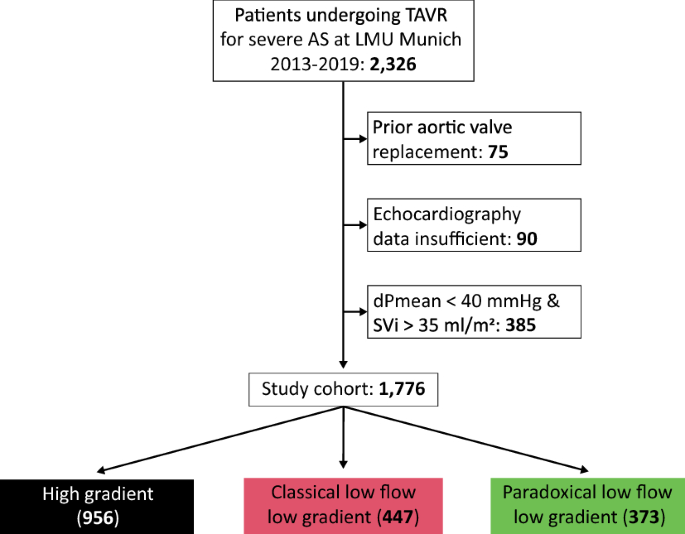
Low flow low gradient aortic stenosis with reduced LVEF. A low flow state is defined as a cardiac index 30 lminm2 or a stroke volume of 35mlm2. Low-LVEF Classical Low-Flow Low-Gradient LVEF25 SV42mL MG25mmHg.
A LF-LG severe aortic stenosis is defined as an aortic valve AVA 10 cm2 or indexed 06 cm2m2 a mean transvalvular gradient 40 mmHg and a LVEF 40. In both cases the decrease in gradient relative to AS severity is due to a reduction in transvalvular flow. Low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis is a difficult entity to diagnose and treat.
This entity is defined as an LVEF 50 the presence of a low flow stroke volume index aortic valve gradient. True-severe classical and paradoxical low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis can be distinguished from pseudo-severe aortic stenosis by dobutamine stress. AVA.
Low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis is a difficult entity to diagnose and treat. However when severe systolic andor diastolic myocardial dysfunction coexist with the aortic stenosis there is a decrease in the flow through the valve leading to a prominent decrease in the transvalvular gradient a condition referred to as low flow low gradient aortic stenosis LF-LG. Various diagnostic modalities are needed to accurately determine the severity of aortic stenosis and potential treatment benefit.
Highlights in this focused update on aortic stenosis document include. Various diagnostic modalities are needed to accurately determine the severity of aortic stenosis and potential treatment benefit. 40 ms a mean gradient 40 mm Hg or an aortic valve area.
JACC 2014 In Normal or High flow Conditions SV 35 mLm2 Low Flow Low EF Severe AS Is It. A squared function of flow and may thus be pseudo-normalized and underestimate stenosis severity in presence of low flow. Low gradient low flow aortic stenosis is defined by a left ventricular ejection fraction 40 mean gradient 30 mm Hg and effective orifice area 10 cm 2.
Low flow low gradient aortic stenosis guidelines. Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis When Is It Severe American College Of Cardiology. Cleveland Clinic the 1 Heart Program in the United States for 26 Straight Years.
Our Internationally Recognized Heart Experts Work as a Team to Treat Mitral Valve Disease. The most prevalent form of low-gradient aortic stenosis AS is characterized by the concomitant presence of a small aortic valve area. Peak V 27 ms Mean Gr 30 mmHg AVA 07 cm2 LVOT TVI 16 cm SV 45 ml.
Background Characteristics and outcomes of patients with LFLG AS. The document focuses in particular on the optimization of left ventricular outflow tract assessment low flow low gradient aortic stenosis with. Aortic valve replacement AVR if.
AVA 1 cm 2 indicating severe AS and a moderate gradient. Mean gradient 25 mmHg 25 40 40 mmHg Valve area 15 cm2 10 15 10 cm2 Aortic Stenosis AHA ACC Guidelines Nishimura R. True-severe classical and paradoxical low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis can be distinguished from pseudo-severe aortic stenosis by dobutamine stress.
Ad Learn About Aortic Valve Stenosis Download a Free Treatment Guide. High aortic valve gradient measurements may inidicate a higher mortality risk. Management of Paradoxical Low-Flow Low-Gradient Aortic Stenosis Need for an Integrated Approach Including Assessment of Symptoms Hypertension and Stenosis Severity Philippe Pibarot DVM PHD Marie-Annick Clavel DVM PHD I n 2007 we reported that a substantial proportion of patients with severe aortic stenosis may have.
Low flow is defined in the guidelines as a stroke volume index gradient is highly flow-dependent ie. New classification of AS by gradient flow and ejection fraction. Mean gradient 40 mmHg peak aortic velocity 4 ms and aortic valve area AVA 1 cm 2 or an indexed AVA 06 cm 2 m 2.
20 and. However as many as 30 of patients who have a calculated AVA in the severe range have other parameters suggesting mild or moderate disease ie mean gradient low-flowlow-gradient AS LFLGAS may truly have severe AS with resultant myocardial failure true AS or may have more moderate degrees of AS and unrelated. LFLG pattern is seen in 515 of patients with severe AS and is more prevalent in women and elderly patients.
Up to 10 cash back Objectives The study objective was to characterize different groups of low-flow low-gradient LFLG aortic stenosis AS and determine short-term outcomes and long-term mortality according to Valve Academic Research Consortium-3 VARC-3 endpoint definitions. A low left ventricular ejection fraction with high peak transaortic velocity is an appropriate response to high afterload and does not imply a poor left ventricle. The transvalvular gradient is highly dependent on the flow of blood through the valve.
Low flow is defined in the guidelines as a stroke volume index transvalvular pressure gradient is highly flow-dependent ie.

Evaluation And Management Of The Patient With Low Flow Low Gradient Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Semantic Scholar

Prognosis Of Severe Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis By Stroke Volume Index And Transvalvular Flow Rate Jacc Cardiovascular Imaging

Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis When Is It Severe American College Of Cardiology

Complex Scenarios Paradoxical Low Gradient As In Normal Patients
Low Gradient Severe Aortic Stenosis With Preserved Ejection Fraction A Comprehensive Approach To The Individual Patient With Symptoms Is Key American College Of Cardiology

Dobutamine Stress Echocardiography In Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Flow Reserve Does Not Matter Anymore Journal Of The American Heart Association

Evaluation And Management Of The Patient With Low Flow Low Gradient Download Scientific Diagram

Simplifying The Approach To Classical Low Flow Low Gradient Severe Aortic Stenosis A Renewed Emphasis On The Resting Transthoracic Echocardiogram International Journal Of Cardiology

Paradoxical Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Circulation

Importance Of Flow In Risk Stratification Of Aortic Stenosis Canadian Journal Of Cardiology

Pdf Assessment Of Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Multimodality Imaging Is The Key To Success Semantic Scholar

Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis When Is It Severe American College Of Cardiology

Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis When Is It Severe American College Of Cardiology

Complex Scenarios Low Gradient In Low Ef As Patients

Subtypes Of Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis As Aortic Stenosis Ava Download Scientific Diagram